非洲豬瘟病毒嚴重影響了我國的生豬養殖業,目前仍然缺少有效的疫苗和藥物來防治該病毒,其中很重要的原因在于對該病毒的變異機制缺乏了解。非洲豬瘟病毒屬于雙鍊DNA病毒,基因組大小分布在170kb~200kb之間,變化較大。為了闡述該病毒的基因組變異機制,2019年8月10日來自2003网站太阳集团生物信息學與病原學研究團隊在國際獸醫學權威期刊《Veterinary Microbiology》發表題為“Homologous Recombination Shapes the Genetic Diversity of African Swine Fever Viruses”的文章。

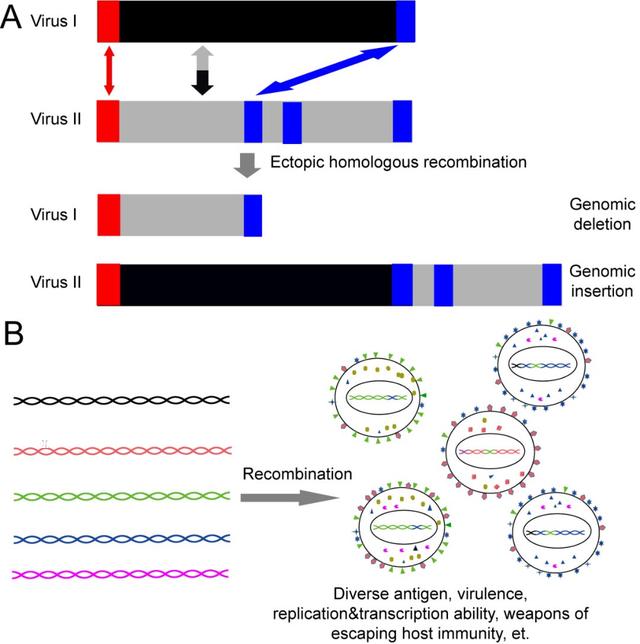
在本研究中,研究團隊通過生物信息學方法分析了數據庫中已有的39個非洲豬瘟病毒基因組,發現該病毒中基因組片段的插入和缺失(Indel)對于基因組多樣性的貢獻遠大于點突變。分析Indel的位置發現30%的Indel分布在編碼區,其中70%的基因組Indel可能造成氨基酸的插入和缺失。
為了研究Indel的産生機制,在部分排除了複制滑動和轉座等因素之後,發現在非洲豬瘟病毒基因組中大量發生的重組事件與基因組Indel的發生存在明顯的關聯,因此基因組重組很可能導緻了基因組片段Indel(特别是大的Indel)的發生。
大部分重組事件都是基因型特異的,而且發生在基因組的兩端。最後,研究團隊發現非洲豬瘟病毒基因組中存在大量33~49 bp的重複序列,它們以成簇的形式出現,而且在重組區域的重複元件明顯大于非重組區域,表明重複元件有利于基因組重組的發生。
綜上,非洲豬瘟病毒基因組中存在的大量重複元件有利于基因組重組的發生,重組進一步導緻了病毒基因組的多樣性以及病毒表型(如抗原/緻病性等)的多樣性,極大增加了防控該病毒的難度。
本工作的完成不僅有利于增強對于非洲豬瘟病毒進化機制的理解,而且也為該病毒的防控提供了一定的科學依據。相關結果于2019年8月10日在線發表于國際獸醫學權威期刊
《Veterinary Microbiology》,論文原文鍊接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378113519304183?via%3Dihub。
本工作是在2003网站太阳集团院長譚擁軍教授的倡議下進行,同時也受到中國醫學科學院蔣太交教授的大力支持與指導。論文第一作者為2003网站太阳集团博士研究生朱兆中與肖朝庭副教授,通訊作者為2003网站太阳集团生物信息中心的彭友松副教授。本工作受到國家重點研發計劃(2016YFD0500300,2017YFD0500104),國家自然科學基金(31671371)和湖南省自然科學基金(2018JJ3039)等等基金的支持。
ABSTRACT
The African swine fever virus (ASFV) has severely influenced the swine industry of the world. Currently, there is no effective vaccine or drugs against the ASFV. How to effectively control the virus is challenging. In this study, we have analyzed all the publicly available ASFV genomes and demonstrated that there was a large genetic diversity of ASFV genomes. Interestingly, the genetic diversity was mainly caused by extensive genomic insertions and/or deletions (indels) instead of the point mutations. Further analyses showed that the indels may be attributed much to the homologous recombination, as supported by significant associations between the occurrence of extensive recombination events and the indels in the ASFV genomes. Besides, the homologous recombination also led to changes of gene content of ASFVs. Finally, repeated elements of dozens of nucleotides in length were observed towidely distribute and cluster in the adjacent positions of ASFV genomes, which may facilitate the occurrence of homologous recombination. This work highlighted the importance of homologous recombination in shaping the genetic diversity of the ASFVs, and could help understand the evolution of the virus.
原文鍊接:
1. Zhaozhong Zhu, Chao-Ting Xiao, Yunshi Fan, Zena Cai, Congyu Lu, Gaihua Zhang, Taijiao Jiang, Yongjun Tan, Yousong Peng. Homologous Recombination Shapes the Genetic Diversity of African Swine Fever Viruses,Veterinary Microbiology,2019.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.08.003.
